A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Click a letter to see a list of conditions beginning with that letter.
Click 'Topic Index' to return to the index for the current topic.
Click 'Library Index' to return to the listing of all topics.
Testicular Appendage Torsion
Testicular appendage torsion is the twisting of a small piece of tissue above a testicle. The appendage doesn’t have a function in the body. But it can twist and cause pain and swelling that gets worse over time. It's not the same as testicular torsion. It's not a medical emergency like testicular torsion.
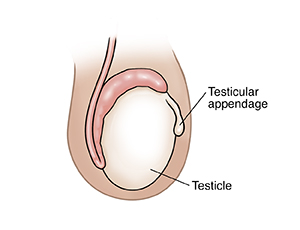
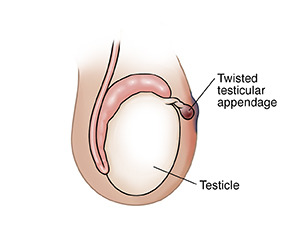
What causes testicular appendage torsion?
Appendage torsion can happen at any time. It’s most likely to happen during sleep. And it's more likely in preteen boys. When the appendage gets twisted, it cuts off its own blood supply. This doesn’t cause any serious damage.
Is it the same as testicular torsion?
Testicular appendage torsion is not the same thing as testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is the twisting of the testicle. This is a medical emergency. The torsion causes a loss of blood supply to the testicle. Surgery is needed right away to prevent lifelong (permanent) damage. The symptoms can be similar in both conditions. But the pain of testicular torsion is often more severe.
Symptoms of testicular appendage torsion
Symptoms can include:
-
Pain in one testicle, on one side of the scrotum
-
Swelling and redness of the scrotum
-
Scrotum that’s sore to the touch
-
A hard lump at the top of the scrotum
-
A blue dot at the top of the scrotum, which shows that the twist is in the appendage, not the testicle
How is testicular appendage torsion diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your health history and your symptoms. You’ll be given a physical exam. You may also have tests such as:
-
Urine test. This is to check for other possible causes of scrotal pain, such as infection.
-
Imaging test of your scrotum. This may include an ultrasound.
In some cases, you may need surgery right away if it seems like you may have testicular torsion. This is to help prevent severe problems. During surgery, the healthcare provider will be able to see if the condition is testicular appendage torsion.
Treatment for testicular appendage torsion
Treatment for testicular appendage torsion includes:
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider right away if you:
When to seek emergency medical care
Sudden testicular pain may be a medical emergency. See a healthcare provider and get checked right away.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Melinda Murray Ratini DO
Online Medical Reviewer:
Raymond Turley Jr PA-C
Online Medical Reviewer:
Tara Novick BSN MSN
Date Last Reviewed:
9/1/2025
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.