A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Click a letter to see a list of conditions beginning with that letter.
Click 'Topic Index' to return to the index for the current topic.
Click 'Library Index' to return to the listing of all topics.
Hematuria: Possible Causes
Many things can lead to blood in the urine (hematuria). The blood may be easy to see when you look at the urine. This is called gross hematuria. Urine may appear clear and blood may only be seen when looked at under a microscope. This is called microscopic hematuria. Often no cause for the blood can be found. This is called idiopathic hematuria. Here are some of the most common causes of blood in the urine:
-
Kidney or bladder stones. These are deposits of minerals and salts. Stones may be found anywhere in the urinary tract. Stones most often form in the kidneys. Much less often they form in the bladder. In addition to blood in the urine, they can cause severe pain.
-
BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia). This is enlargement of the prostate gland. It happens with age. BPH often causes problems with urination. It sometimes causes blood in the urine.
-
Urinary tract infection. This is due to bacteria growing in the urinary tract. It can cause blood in the urine. Other symptoms include burning or pain with urination. You may need to urinate often or urgently. You may also have a fever.
-
Damage to the urinary tract. This damage may be due to an injury or trauma. It may also result from the use of a urinary catheter. Vigorous exercise may sometimes irritate the urinary tract and cause bleeding.
-
Cancer anywhere in the urinary tract. A tumor may sometimes cause no symptoms other than bleeding.
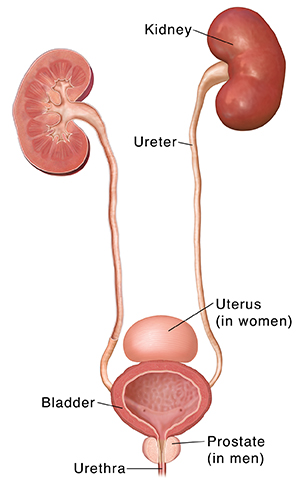
Other possible causes of bleeding include:
-
Prostate gland infection (prostatitis)
-
Taking anticoagulants
-
Blood clotting disorders such as hemophilia
-
Blockage in the urinary tract
-
Kidney disease or inflammation
-
Cystic diseases of the kidneys
-
Sickle cell anemia
-
Endometriosis
Online Medical Reviewer:
Marc Greenstein MD
Online Medical Reviewer:
Michelle Anderson DNP
Online Medical Reviewer:
Raymond Kent Turley BSN MSN RN
Date Last Reviewed:
9/1/2025
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.