Understanding Blighted Ovum
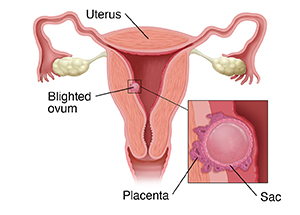
Blighted ovum is a type of early pregnancy loss. It’s also called anembryonic pregnancy or empty sac. You have a placenta and a gestational sac, but the embryo doesn’t grow. The placenta and sac still give off pregnancy hormones. These cause a pregnancy test to show positive. And you can have pregnancy symptoms. Because of this, the pregnancy loss often isn’t found until an ultrasound is done later in pregnancy.
How to say it
BLI-tehd OH-vuhm
What causes blighted ovum?
In most cases, the cause is abnormal chromosomes in the fertilized egg. Other possible causes include:
-
An infection
-
An autoimmune disease in the parent
-
An endocrine disease in the parent
-
Tissue that divides the inside of the uterus into sections (septum)
Symptoms of blighted ovum
Treatment for blighted ovum
After a pregnancy loss, the placenta and sac need to leave the body. The process can cause pain and bleeding. This can happen on its own, or your body may need help. Your healthcare provider may advise any of the treatments below:
-
Expectant management. This means to watch and wait. If it’s safe for you, your healthcare provider may advise waiting several weeks to see if the placenta and sac are released from your uterus on their own.
-
Medicine. The medicine misoprostol can help the process. You may take the medicine by mouth. Or it may be put into your vagina. You may also be given pain medicine to help lessen abdominal cramping.
-
Uterine evacuation/curettage. You are given pain medicine, plus medicine to help you relax and feel sleepy. A tube is put through the opening of the vagina and cervix. The tube is attached to a vacuum device. The device creates suction that helps remove the tissue. In some cases, a tool called a curette is used to help loosen tissue in the uterus first.
After or during the treatment, you may need to have an ultrasound test. This is to make sure all the tissue has left your body.
You will also need emotional support during and after this process. Losing a pregnancy is very upsetting. Talk with your healthcare provider and your family to get support during this time. You may want to speak with a counselor or attend a support group. Make sure to ask for any help you need.
Possible complications of blighted ovum
Possible problems can occur from treatment. These can include:
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these:
-
A lot of bleeding from your vagina
-
Dizziness or fainting
-
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your provider
-
Other symptoms that don’t get better, or get worse
-
Severe pain that isn’t helped with pain medicine
Online Medical Reviewer:
Donna Freeborn PhD CNM FNP
Online Medical Reviewer:
Heather M Trevino BSN RNC
Online Medical Reviewer:
Irina Burd MD PhD
Date Last Reviewed:
6/1/2022
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.