Treating Metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia is pain in the "ball of your foot," the area between your arch and your toes. The pain usually starts in one or more of the five bones in this area under the toes. These bones are called the metatarsals. The metatarsals become inflamed. This causes the pain. Often, a callus builds up in this area. Calluses are a flat, widespread thickening of the outer layer of skin. In most cases, wearing low-heeled, well-cushioned shoes and filing down the callus will ease the pain. If these steps don’t work, you may need to do exercises or have surgery to remove part of the bone. To take pressure off the ball of your foot and ease the pain, your healthcare provider may suggest that you do one or more of the following.
Wear shoes with padded soles
Wear shoes with thick padding in the soles. Keep heels low. Make sure the shoe is wide across the ball of your foot and your toes. Don't wear shoes that don't fit well.
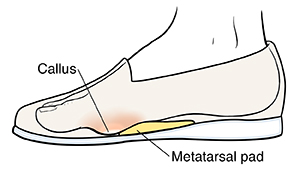
Using a metatarsal pad
Put a metatarsal pad in your shoe. This lifts and takes pressure off the painful area. To insert the pad:
-
Put a small lipstick mark on the callus.
-
Step into the shoe to leave a mark on the insole.
-
Peel the backing off the pad. Then put the pad in the shoe just behind the lipstick mark.
You may also be able to find inserts with built-in metatarsal pads.
Filing the callus
-
Soak your foot in warm water for a few minutes to soften the skin.
-
Dry the foot.
-
Gently rub the callus with a pumice stone or nail file to remove the hard skin. Stop if bleeding or pain occurs.
If you have diabetes, see your diabetes healthcare provider for foot care.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Rahul Banerjee MD
Online Medical Reviewer:
Raymond Turley Jr PA-C
Online Medical Reviewer:
Stacey Wojcik MBA BSN RN
Date Last Reviewed:
8/1/2023
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.