A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Click a letter to see a list of conditions beginning with that letter.
Click 'Topic Index' to return to the index for the current topic.
Click 'Library Index' to return to the listing of all topics.
Urinary Tract Infections in Men
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are most often caused by bacteria that invade the urinary tract. The bacteria may come from outside the body. Or they may travel from the skin outside of the rectum into the urethra. Pain in or around the urinary tract is a common symptom for most UTIs. Other symptoms of a UTI may include pain when peeing, blood in the pee, flank or groin pain, chills and a fever, and nausea and vomiting. The only way to know for sure if you have a UTI is to have a urinalysis and urine culture.
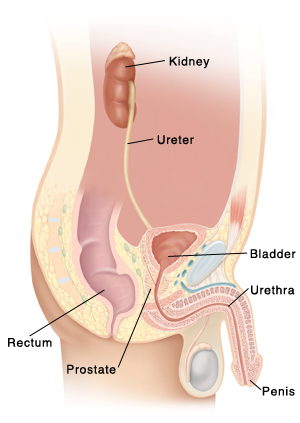
Types of UTIs
-
Cystitis. This is a bladder infection. It's often caused by a blockage from an enlarged prostate. You may have an urgent or frequent need to pee. You may have bloody pee. Treatment includes antibiotics and medicine to relax or shrink the prostate. Some people need surgery.
-
Urethritis. This is an infection of the urethra. You may have fluid from the urethra or a burning feeling when you pee. You may have pain in the urethra or penis. It's treated with antibiotics.
-
Prostatitis. This is an inflammation or infection of the prostate. You may have an urgent or frequent need to pee, a burning feeling when you pee, or a fever. Or you may have a sore prostate or a vague feeling of pressure. Prostatitis is treated with a range of medicines. This depends on the cause.
-
Pyelonephritis. This is a kidney infection. If not treated, it can be serious and damage your kidneys. In severe cases, you may need to stay in the hospital. You may have a fever and low back pain.
Medicines to treat a UTI
Most UTIs are treated with antibiotics. These kill the bacteria. The length of time you need to take them depends on the type of infection. Take antibiotics exactly as directed until all of the medicine is gone, even if you feel better. If you don't, the infection may not go away. It may become harder to treat. For some types of UTIs, you may be given other medicine to help treat your symptoms.
Self-care to treat and prevent UTIs
The lifestyle changes below will help get rid of your infection. They may help prevent future UTIs.
-
Drink plenty of fluids. This includes water, juice, or other caffeine-free drinks. This helps flush bacteria out of your system.
-
Empty your bladder when you feel the urge to pee and before going to sleep. Pee that stays in your bladder promotes infection.
-
Use condoms during sex. These help prevent UTIs caused by bacteria spread from sex.
-
Keep follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider. They may do tests to make sure the infection has cleared. If needed, more treatment can be started.
Other treatments
Most UTIs respond to medicine. Some people need a procedure or surgery. This may be done to treat an enlarged prostate. Or it can remove a kidney stone or other blockage. Surgery can be done to treat problems caused by scarring or long-term infections.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Chris Southard RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Melinda Murray Ratini DO
Online Medical Reviewer:
Rita Sather RN
Date Last Reviewed:
3/1/2024
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.